Warehouse automation deployment mainly aims at improvement and significant acceleration of processes and human work reduction. Warehouse automation covers sets of automatically controlled devices of the storage systems including racks, lifts and shuttles, internal transportation systems such as conveyors, AGV (automatic guided vehicles) or AMR (autonomous mobile robots), other robots (e.g. palletizers) or cobots and related software. All these elements support or carry out independently certain warehouse processes, like receiving, storage, picking, sorting and shipment.
Service provision process
01 AUTOMATION DEPLOYMENT BUSINESS CASE
Verifying potential and needs for automation, assumptions for the automation project
02 AUTOMATED WAREHOUSE MASTERPLAN
Optimal logistics concept, layout, technology selection, CAPEX, OPEX and ROI calculations
03 SOLUTIONS AND SOFTWARE DETAILED PLANNING
Equipment and solutions specification, WMS design, tender documentation
04 IMPLEMENTATION OF WAREHOUSE AUTOMATION
Supervision of purchases, assembly and commissioning, until the planned performance is achieved
A business approach to automation
- Taking into account business objectives and sales development directions of the company
- Concepts independent form vendors - objectivity of investment decisions and competitiveness in tenders
- Flexibility and rationality of implemented solutions, including expansion and staging of investment projects
- Comparative ROI calculations of various technology solutions, including TCO (total cost of ownership)
- Verification of technology availability and installation requirements through an open technical dialogue with potential suppliers
- Roadmap of implementation and risk analysis including linkages with other functions of the organization
- Clear communication for decision makers facilitating the investment decision-making process

Automation deployment effects
- Acceleration of warehouse operations
- Higher service level - possibility to provide additional services in the time saved
- Better usage of warehouse space
- Reduction of human labour outlays
- Better control of processes, full tracking and reduction of errors
- Ability to handle sudden sales peaks without losing process quality
- Limitation of lost sales
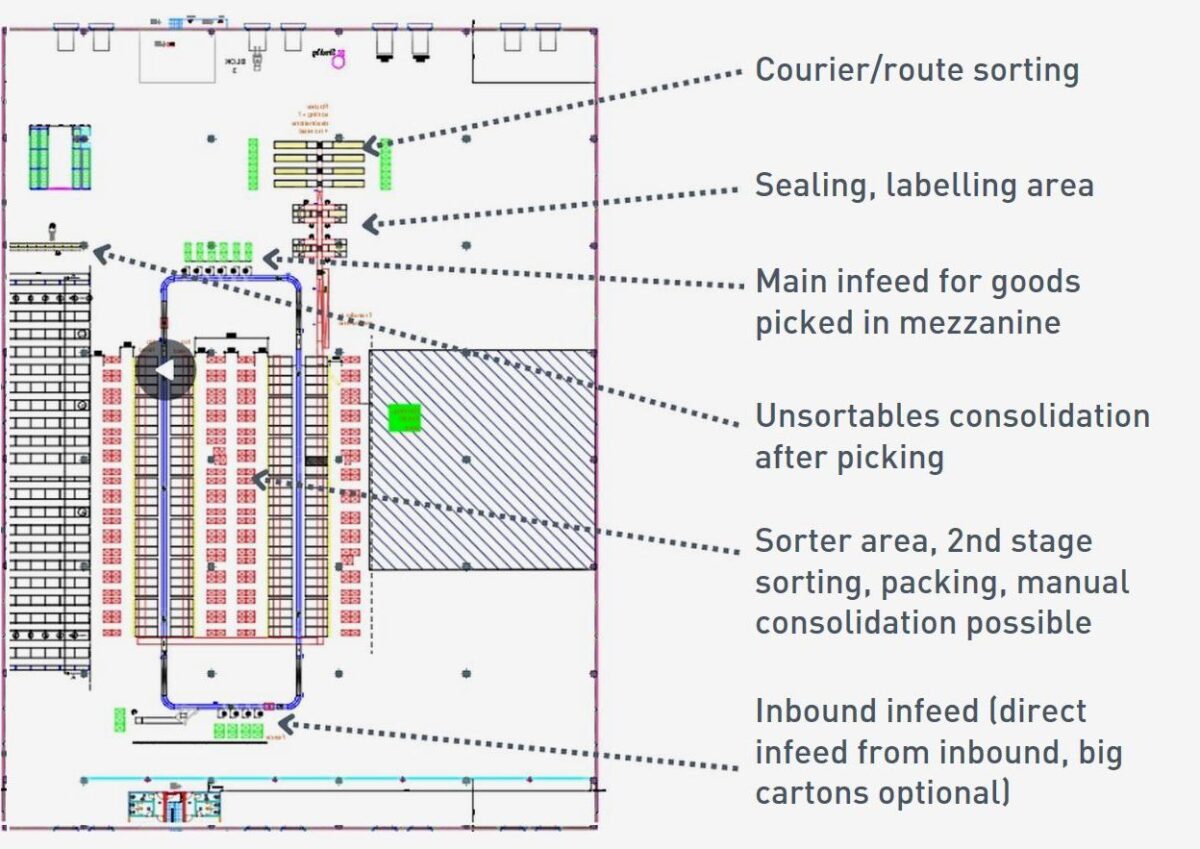
Case study
Sorting capacity for a shipment of 60 thousand units per day and a shortened cut-off time from a logistics centre in Serbia.

In the eye of an expert

One of the key parameters when deciding to automate a warehouse, although difficult to calculate precisely, is the value of lost sales due to slower implementation, non optimal resources and, above all, lower service level. Therefore, the most common practice, is to analyze alternative costs, such as higher labour outlays or storage space and return on investment time.
Łukasz Musialski
Senior Consultant
Contact regarding the offer

Bartosz Jacyna
Partner, Business Development
Other key services

